Project Management
Useful Links
Responsibilities
It is the responsibility of the Chief Product Officer (CPO) to manage and plan the work being conducted by the development team.
The CPO will account for the number of developers available in a given sprint to define the capacity. Each item planned will have an associated number of points assigned to it, to define an estimated sizing.
Planning
Scheduling
ESPROFILER operates with a 2-week sprint cycle. This is a fixed length of time that is used to plan and track work items. It allows for regular review and adjustment of our plans, and ensures that we have traceable progress towards our goals. Sprints have the following structure:
- 2 Weeks Long
- Begin on a Monday
- End on a Friday
- Naming convention will be kept simple with a incremental number system, e.g.
Sprint 1,Sprint 2 - Capacity defined as a number of points.
Releases
TBC
Work Items
Jira operates on the principle of a work item (formerly known as issues). These track individual pieces of work to be done by team members. They can represent larger roadmap items as part of product roadmap planning, down to small bugs reported on the platform.
Types
Each Work Item has a "type", which distinguishes it's associated properties and functionality, and defines whee the work item lives in the hierarchy of work items.
Cross-Project Work Items
These tasks are created and managed in the "PLAN | Design & Planning" Space.
- Initiatives: Long-term goals and ideas. These can be new applications, signficant feature sets, or other large-scale projects. These may not have fixed outcomes, and can evolve over time, but help define our long term roadmap.
- Story: A user-focussed and scoped piece of work. These are generally requiring multiple elements to be implemented in order to be completed that would span across multiple projects, e.g. front-end and back-end services.
Project-Scoped Work Items
These work items are then created in individual spaces associated with each project/repository, e.g. App | Platform for Front-End work, or API | Platform for Back-End work.
- Tasks: Focussed, sized, actionable items that have a clear, achievable outcome. These are scoped to single projects.
- Subtasks: Work items that are used to break down tasks if they need to be split into smaller, more manageable pieces, and distributed across a team. It is best practice to avoid these where possible, and instead use Tasks.
Stories
Stories should contain a user-centric description of a feature or set of features that are to be implemented. They should follow the structure of:
As a [user persona], I want to [achieve a goal], So that [benefit to the user]
Epics should be unique, the I want statement especially should be something that the user cannot achieve right now, but can achieve with the Epic being implemented.
Tasks
Tasks should be sized such that they are assignable and actionable by a single person. They are scoped to a single project.
Tasks should have enough detail in them so that whomever is assigned can start working on it immediately, and do so without needing additional context or clarification. If additional details are required, questions and comments should be added to the tasks themselves per our Asynchronous Communication guidelines.
Hierarchy
The hierarchy of work items is as follows, where the top-level item is the Initiative, and the bottom-level item is the Subtask. It is possible to have work items from the lower levels that do not have a parent item, e.g. a Bug report, or small chore task.
- Initiatives
- Stories
- Tasks
- Subtasks
Creating Work Items
You can click the "+ Create" button at the top of Jira's navigation in order to create a new Work Item.
Work Items should provide enough detail that they are actionable. If additional details are required, questions and comments should be added to the tasks themselves per our Asynchronous Communication guidelines, not in other communication channels, this ensures that other observers of the item also have access to the information.
Spaces
The first field you need to select when creating a new Work Item is the "Space" field.
Spaces are used in Jira to separate work items into buckets that, in our case, align to the different components (often repositories) of ESPROFILER. Work Items opened in a given space will be given a particular prefix to their ID, e.g. ESPF-123 for a work item opened in the ESPF (ESPROFILER Platform Front-End) space.
These spaces are independent of function, and span across all projects:
- PLAN | Design & Planning (PLAN): This space is used for creating work items that span multiple projects. This is the home of all Initiatives and Stories.
- Other (OTHER): This space is used for creating tasks that are not scoped to a specific project, e.g. documentation, admin tasks, or setting up accounts for third-party services.
Front-End Spaces:
- FE | Platform (ESPF): This space is used for creating work items that are scoped to the Front-End of the ESPROFILER Platform.
- FE | Central Authentication Service (CASF): The Central Authentication Service (CAS) Front-End.
- FE | CDM Builder (CDMF): The Capability Exchange CDM Builder Front-End.
- FE | Vendor Portal (EXCF): The Vendor Portal (Front-End) for the Capability Exchange.
Back-End Spaces:
- API | Platform Service (ESPB): Monolithic application that is the core of the ESPROFILER Platform.
- API | Libraries (DBL): Shared services and libraries that are used across all back-end projects.
- API | Central Services (EXCB): Shared tenancy services that are available via
https://api.esprofiler.com.
Other Spaces:
- Design Lab (DESIGN): This space is used for creating work items that need to be completed by a Designer, e.g. visual design, branding, or other design-related tasks.
- DATA | Science & Tasks (DPE): This space is used for creating work items that are scoped to the Data Provisioning Environment (DPE), and are often completed by the Data Science and Analytics team, e.g. customer onboarding & discovery, data analysis, and other data-related tasks.
- Compliance (CL): Action items from audits, issues rasied by customers for compliance, etc.
- Infrastructure (INFRA): Work items that are scoped to the infrastructure of the platforms we operate, e.g. AWS.
Prioritisation
Each work item can be assigned a priority to help product management and engineers decide where to focus their efforts when looking for new work to do. The priorities use are:
- Critical: This is used for urgent changes that require engineering to drop all other tasks. Most commonly this will be associated against platform-breaking problems that need to be resolved as soon as possible.
- High: These items should be front and center in Product Planning. This should be used for pulling attention to the most important items in sprint planning and the backlog.
- Medium: Should be getting into the product sooner rather than later, but there is not an immediate urgency.
- Low: (default) These are items are up for consideration, and could be addressed at some point, but there is no urgency.
Sizing Work Items
Work items are sized in points. These are estimated sizings helped to provide guidance on how long items should take. These help with project planning and ensuring we have planned to our capacity. These do not set deadlines, and should be sized in isolation of other work items.
Initial sizings will be done at the Story level, then, when individual tasks are created, each task will have an associated number of points assigned to it, to provide a more accurate estimate of the total effort required.
Sizings should use the following scale:
- Tiny - 0.5: This is used for small, quick tasks that can be completed less than half a day.
- Extra Small - 1: Work items that are estimated to take about 1 day.
- Small - 2: Work items that are estimated to take about 2 days.
- Medium - 3: Work items that are estimated to take about 3 days.
- Large - 5: Work items that are estimated to take about 3-5 days.
- Extra Large - 8: Work items that are estimated to take about 5-8 days.
- Huge - 13: Work items that are estimated to take more than 8 days.
Kanban Boards
A very useful view in Jira is the Kanban Board. It splits work items into columns, where these columns indicate progress. The further to the right a work item is, the closer to completion it is.
We have a number of Kanban boards available to view and use in Jira:
- Product Roadmap Board: Used for tracking the long-term roadmap of the product, focussing on larger Initiatives and Epics.
- Development Board - Active Sprint: Used for tracking short-term work items that are currently being worked on, or scheduled in the current sprint.
- Development Board - Full Backlog: Used for exploring all work items across all projects.
Product Roadmap Board
Link: Product Roadmap Board
Used for tracking the long-term roadmap of the product, focussing on larger Initiatives and Epics. Work Items in this board can be moved between the following states:
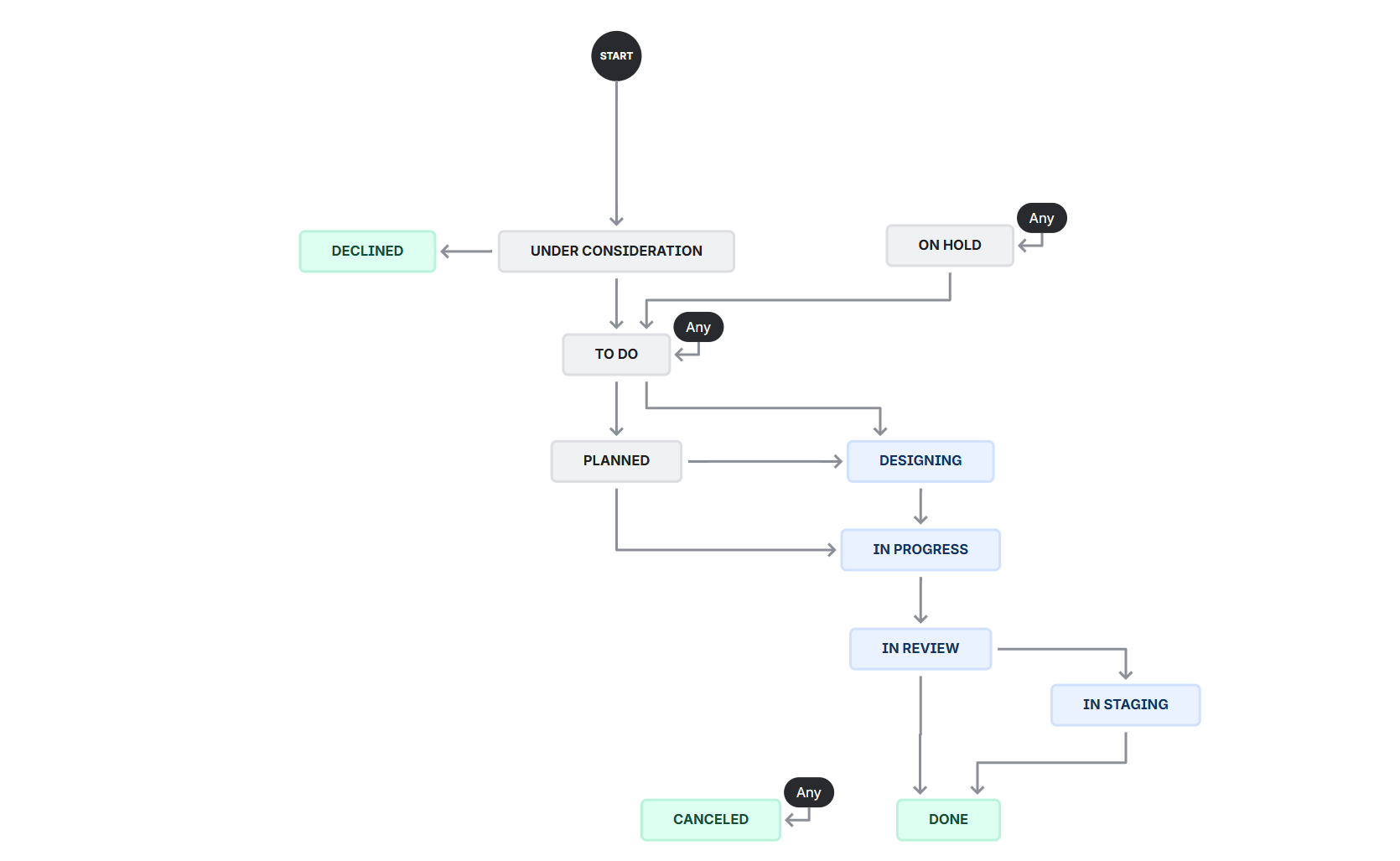 Screenshot of the Workflow Editor from Jira that defines the statuses available for Initiativess.
Screenshot of the Workflow Editor from Jira that defines the statuses available for Initiativess.
- Under Consideration: This is a new idea, and is to be discussed by the Leadership Team as to whether it is something we should build into ESPROFILER.
- Declined: This is an idea that has been discussed and decided against.
- To Do: This ideas has been reviewed, and considered valuable for ESPROFILER. In this state it is now part of the Product Backlog.
- Planned: This ideas has now been scheduled for development. This could be imminent (part of an upcoming Sprint) or further out (part of the Product Roadmap.).
- Designing: The idea is either in a design pahase, either with Engineers (to work out technical design elements) or with Designers (to work out visual design elements).
- In Progress: The work item is actively being developed.
- In Review: Development has been complete, and is now being reviewed and QA tested by another engineer.
- In Staging: The work item has been tested and has been deployed to our staging environment for final QA.
- Done: The work item has been completed and is now ready for release.
- On Hold: There is a blocker on this work item progressing.
- Cancelled: The work item has been cancelled and is no longer being worked on.
Development Board
Link: Development Board - Active Sprint
The Development Board is used to track the work items that are currently being worked on and scheduled in the current sprint.
Work Items at this level are assigned to a single engineer, and will have fixed sizings on how much effort we think they should take. Work items in this board can exist in one of the following states:
Work Item Status
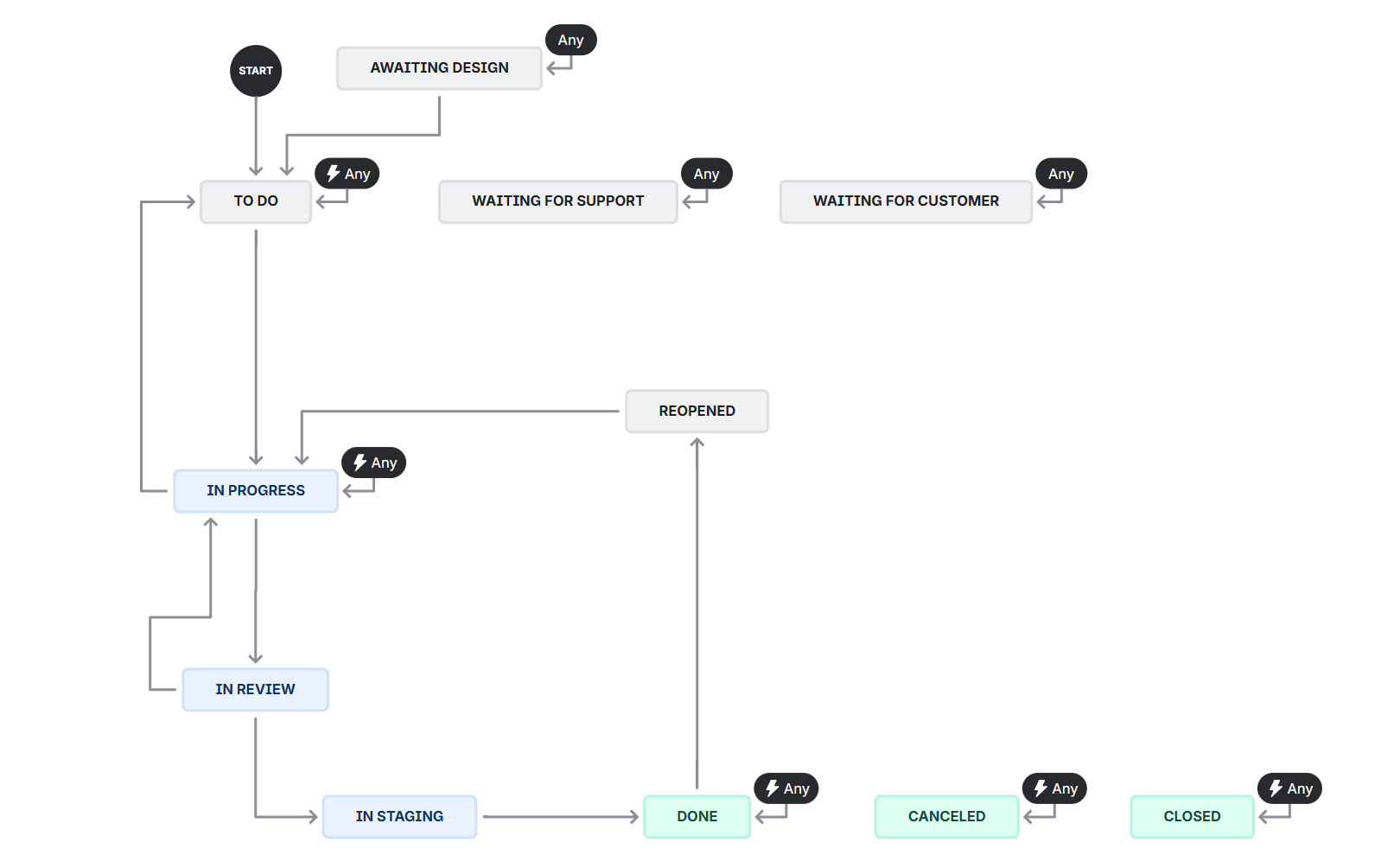 Screenshot of the Workflow Editor from Jira that defines the statuses available for Tasks & Subtasks.
Screenshot of the Workflow Editor from Jira that defines the statuses available for Tasks & Subtasks.
- Awaiting Design: Development cannot yet begin as we are awaiting visual design elements to be completed.
- Waiting for Customer: Development cannot yet begin as we are awaiting customer approval or input.
- To Do: This item has not yet been started, but is able to when an engineer becomes free.
- In Progress: Active development effort has started on this work item.
- Waiting for Support: Development is blocked as the assigned engineer needs assistance.
- In Review: Development has been complete, and is now being reviewed and QA tested by another engineer.
- Reopened: Issues have been found after this work item was classified as "Done" and needs to be re-worked.
- In Staging: The work item has been tested and has been deployed to our staging environment for final QA.
- Done: This item has no outstanding tasks remaining and is completed.
- Cancelled: The work item has been cancelled and is no longer being worked on.
- Closed: The work item has been closed and is no longer being worked on, but the reasoning does not align with any other status.
Status
At ESPROFILER, we use the following columns to represent a work item's status:
- To Do: This item has not yet been started
- In Design: This item is either in-design for visual elements, or in engineering-design/planning, e.g. architectural design
- In Development: Active development effort has started on this work item.
- Development Complete: The assigned engineer has completed the development effort and it is now under review and in QA.
- Done: This item has no outstanding tasks remaining and is completed.
Closing Work Items
Work Items are considered completed when transitioned to the "Done" status. For development tasks (which is all work items except for "Design", "Data" and "Other") Work Items should have a 1:1 relationship with a Merge Request, and be explicitely linked to the Merge Request in Jira.
